Are you struggling to access WIC benefits because your income exceeds the standard eligibility limits? You're not alone. Many families face challenges when their income is slightly above the threshold but still struggle to meet basic nutritional needs. The Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC) is a vital resource for ensuring the health and well-being of mothers and young children. However, navigating the eligibility criteria can be confusing, especially if your income is higher than the standard guidelines. This article will provide you with actionable strategies to explore your options and potentially qualify for WIC benefits despite a higher income.
WIC is a federally funded program designed to support low-income families by providing nutritious food, healthcare referrals, and nutrition education. While the program has strict income limits, there are exceptions and alternative pathways that may still allow you to qualify. Understanding these nuances can make a significant difference in accessing the resources you need. In this guide, we'll walk you through the eligibility criteria, explore exceptions, and offer practical advice to help you navigate the system.
In the following sections, we’ll cover everything from the basics of WIC eligibility to lesser-known exceptions and strategies for maximizing your chances of approval. Whether you're a new parent or a caregiver looking to ensure your family’s nutritional needs are met, this article is designed to empower you with the knowledge to make informed decisions. Let’s dive in and uncover how you can access WIC benefits, even if your income is higher than the typical limits.
Read also:What Is Wwe Kane Net Worth In 2023 A Complete Overview
Table of Contents
- Understanding WIC: What It Is and Who It Serves
- WIC Eligibility Criteria: Income and Beyond
- Exceptions to Income Limits: When Higher Income Doesn’t Disqualify
- State Variations in WIC Eligibility Rules
- Alternative Programs for Families with Higher Incomes
- Tips for a Successful WIC Application
- Advocacy and Support: How to Navigate Challenges
- Case Studies: Families Who Overcame Income Barriers
- Data and Statistics: The Impact of WIC on Families
- Conclusion: Taking Action for Your Family’s Nutrition
Understanding WIC: What It Is and Who It Serves
The Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC) is a federal assistance program administered by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). It aims to safeguard the health of low-income pregnant, postpartum, and breastfeeding women, infants, and children up to age five who are at nutritional risk. WIC provides supplemental foods, nutrition education, and referrals to healthcare and social services, making it a cornerstone of support for vulnerable populations.
WIC serves a diverse group of individuals, including pregnant women, breastfeeding mothers, and caregivers of young children. The program focuses on improving health outcomes by addressing nutritional deficiencies and promoting healthy eating habits. Participants receive vouchers or electronic benefits to purchase specific nutritious foods, such as milk, eggs, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables. Additionally, WIC offers breastfeeding support and educational resources to empower families to make informed dietary choices.
Despite its focus on low-income families, WIC is not exclusively limited to those below a specific income threshold. Certain exceptions and state-specific rules may allow families with slightly higher incomes to qualify. Understanding these nuances is essential for maximizing your chances of accessing the program’s benefits.
WIC Eligibility Criteria: Income and Beyond
To qualify for WIC, applicants must meet specific eligibility criteria, including categorical, residential, income, and nutritional risk requirements. Let’s break down each of these components:
Categorical Eligibility
Applicants must fall into one of the following categories:
- Pregnant women
- Postpartum women (up to six months after childbirth)
- Breastfeeding women (up to one year after childbirth)
- Infants and children up to age five
Residential Eligibility
Applicants must reside in the state where they apply for WIC. Proof of residency, such as a utility bill or lease agreement, is typically required during the application process.
Read also:Pisay Pao A Comprehensive Guide To The Delightful Filipino Pastry
Income Eligibility
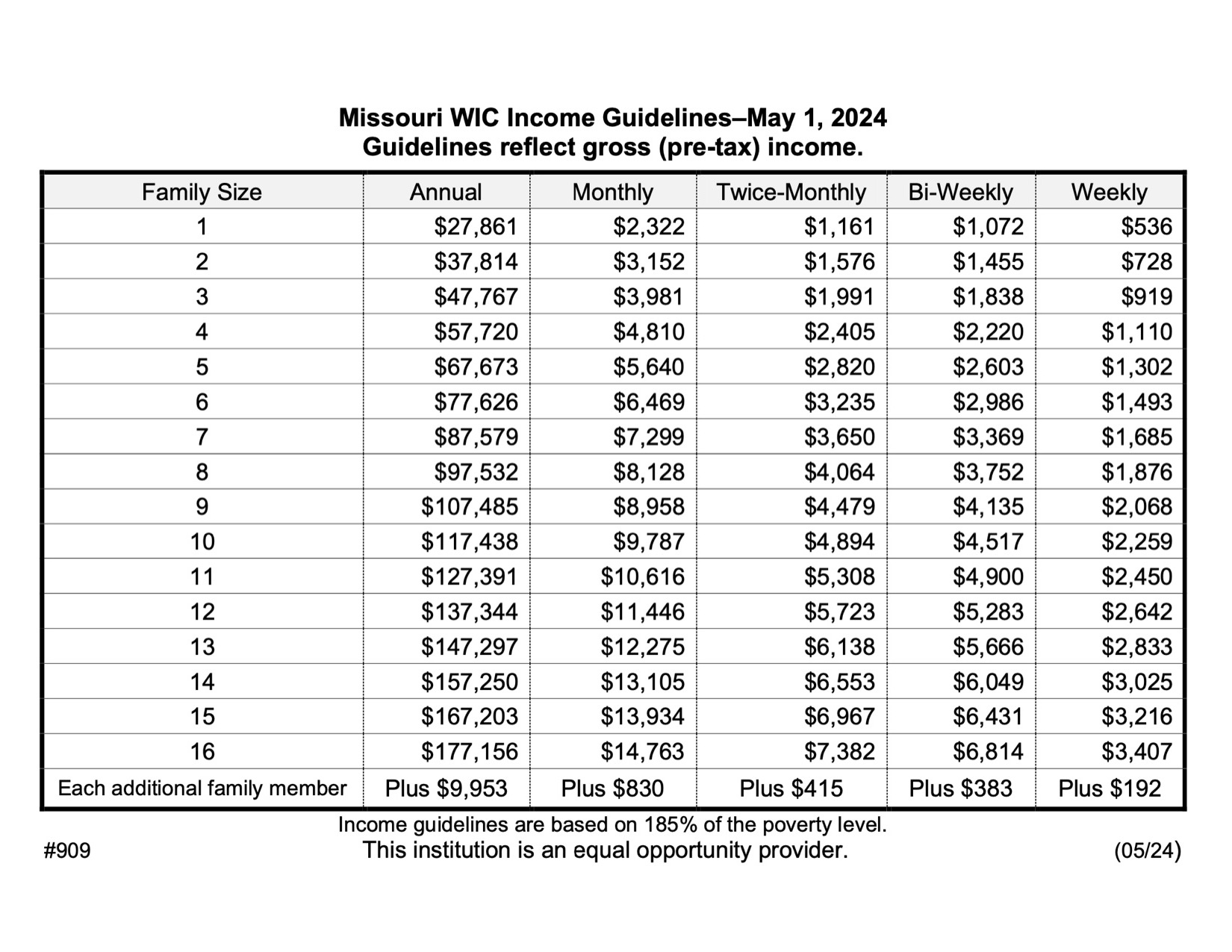
Income is one of the most critical factors in determining WIC eligibility. The program uses federal poverty guidelines to establish income limits, which vary by household size. For example, as of 2023, a family of four must have a gross income of no more than $4,587 per month to qualify. However, some states allow for higher income limits, and certain exceptions may apply.
Nutritional Risk
Applicants must be deemed at "nutritional risk" by a healthcare professional. This can include medical conditions like anemia, underweight, or a history of poor dietary habits. A WIC clinic or authorized healthcare provider typically conducts this assessment during the application process.
Exceptions to Income Limits: When Higher Income Doesn’t Disqualify
While income is a significant factor in WIC eligibility, there are exceptions that may allow families with higher incomes to qualify. These exceptions are often state-specific and depend on individual circumstances. Here are some common scenarios:
Adjunctive Eligibility
Families automatically qualify for WIC if they participate in other federal assistance programs, such as Medicaid, Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), or Temporary Assistance for Needy Families (TANF). These programs have their own income limits, which may be higher than WIC’s standard thresholds.
State-Specific Rules
Some states have higher income limits or offer waivers for families experiencing financial hardship. For example, certain states allow families to qualify if their income is up to 185% of the federal poverty level, compared to the standard 100-185% range.
Medical or Nutritional Hardship
Families with children or caregivers facing significant medical or nutritional challenges may qualify for WIC even if their income exceeds the standard limits. Documentation from a healthcare provider is typically required to support these claims.
State Variations in WIC Eligibility Rules
WIC is administered at the state level, which means eligibility rules can vary significantly depending on where you live. Some states offer more flexibility in income limits, while others have additional requirements or exceptions. For example:
- California: Offers a higher income limit of 200% of the federal poverty level.
- Texas: Allows families to qualify if they participate in Medicaid or SNAP.
- New York: Provides additional support for families with children diagnosed with medical conditions.
It’s essential to check your state’s specific WIC guidelines to understand the available options and exceptions.
Alternative Programs for Families with Higher Incomes
If you don’t qualify for WIC due to income, there are other programs and resources that can help support your family’s nutritional needs:
Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP)
SNAP provides monthly benefits to purchase food and has higher income limits than WIC. Families can use SNAP benefits to buy a wide range of nutritious foods.
Local Food Banks and Pantries
Many communities have food banks and pantries that offer free or low-cost groceries to families in need. These resources often have no income restrictions.
Community Health Programs
Nonprofit organizations and community health programs may offer nutrition education, breastfeeding support, and other services similar to WIC.
Tips for a Successful WIC Application
Applying for WIC can be a straightforward process if you’re well-prepared. Here are some tips to increase your chances of success:
- Gather all necessary documentation, including proof of income, residency, and identity.
- Attend your scheduled appointment with a healthcare provider to assess nutritional risk.
- Be honest and transparent about your financial situation and any challenges you’re facing.
- Reach out to your local WIC office for guidance and clarification on eligibility requirements.
Advocacy and Support: How to Navigate Challenges
If you encounter challenges during the WIC application process, don’t hesitate to seek advocacy and support. Many organizations specialize in helping families navigate public assistance programs. Additionally, connecting with other parents or caregivers who have gone through the process can provide valuable insights and encouragement.
Case Studies: Families Who Overcame Income Barriers
Real-life examples can provide inspiration and practical advice for families facing similar challenges. For instance:
- A single mother in California qualified for WIC through adjunctive eligibility after enrolling in Medicaid.
- A family in Texas accessed WIC benefits despite higher income by documenting their child’s medical condition.
Data and Statistics: The Impact of WIC on Families
Research shows that WIC has a significant positive impact on the health and well-being of participants. According to the USDA, children enrolled in WIC experience improved growth rates, reduced rates of anemia, and better cognitive development. These benefits underscore the importance of accessing WIC benefits, even if your income is slightly above the standard limits.
Conclusion: Taking Action for Your Family’s Nutrition
While WIC has income limits, there are exceptions and alternative pathways that may allow families with higher incomes to qualify. By understanding the eligibility criteria, exploring state-specific rules, and seeking advocacy and support, you can maximize your chances of accessing this vital resource. Remember, WIC is more than just a food assistance program—it’s a lifeline for families striving to provide the best possible start for their children.
If you found this guide helpful, please consider sharing it with others who may benefit. Additionally, feel free to leave a comment or reach out to your local WIC office for further assistance. Together, we can ensure that every family has access to the nutrition and support they need to thrive.