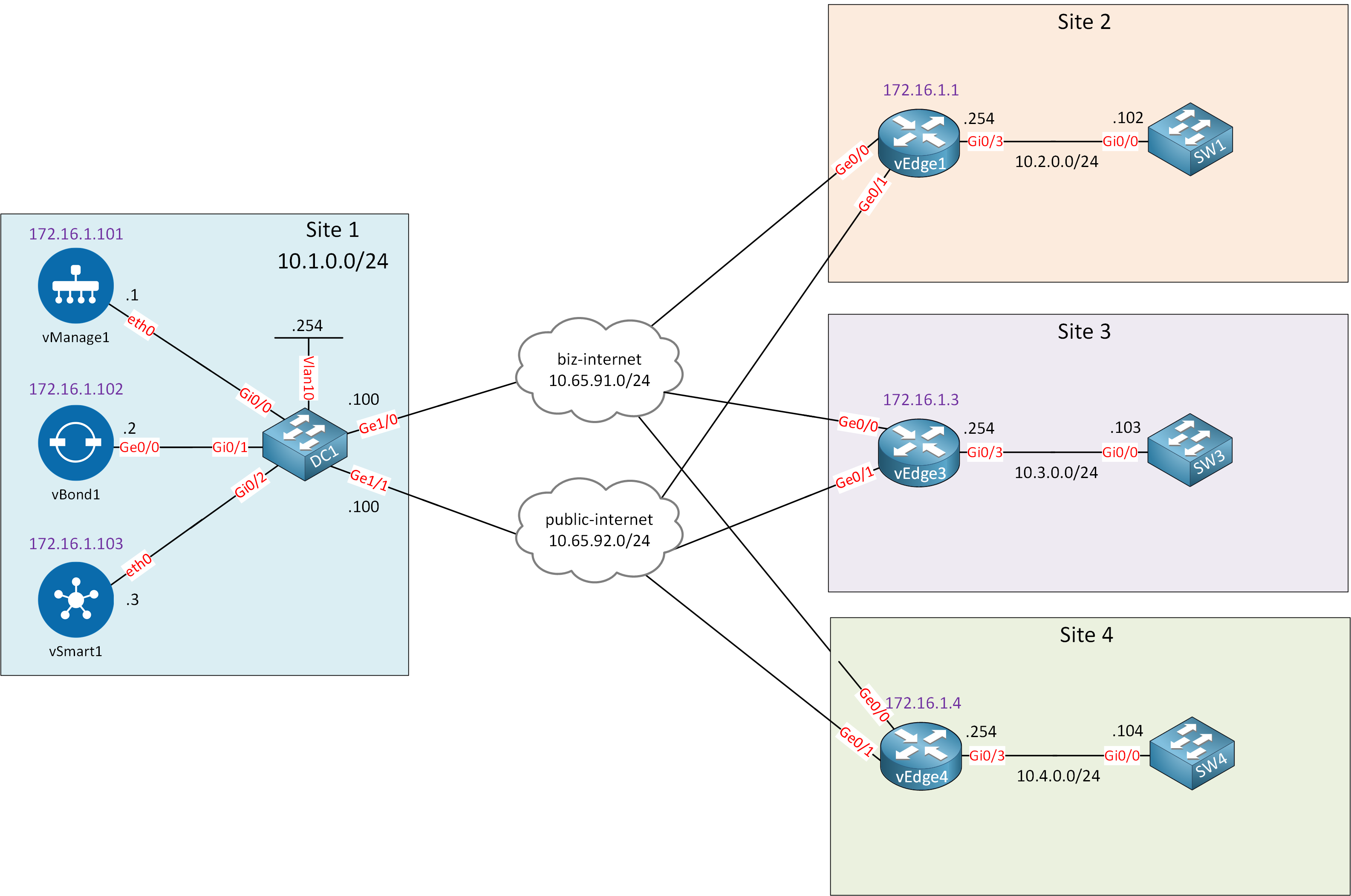
What facilitates seamless data exchange and collaboration within a specific system or industry? A central repository, or "hub," for standardized data points is a crucial element.
A central repository for standardized data points, often within a specific industry or system, allows for easy access, integration, and analysis. These data points could represent various metrics, measurements, or observations. The standardization ensures compatibility and consistency, enabling data from different sources to be combined and analyzed. For instance, a hub might collect and standardize performance data from various manufacturing plants, allowing for company-wide comparisons and optimization strategies.
Such a hub offers several significant benefits. Standardized data facilitates the identification of trends and patterns, enabling proactive decision-making and process improvement. Improved communication and collaboration are also possible, as data is readily accessible and consistent across teams. The historical context suggests that as data volume and complexity grow, such a central point for aggregation and standardization becomes increasingly essential. Rapid analysis of vast data sets becomes possible, which drives innovation and efficiency. This approach reduces redundancy and ensures the quality and reliability of data used for decision-making.
Read also:Is Sona Bella Autistic Unveiling The Truth Behind The Popular Tiktok Sensation
Now let's delve into specific applications and use cases of this data repository concept in various industries. We will examine how this centralized platform optimizes processes and improves decision-making across different sectors.
SD Point Hub
A well-structured "SD Point Hub" is critical for efficient data management and analysis. Its effectiveness hinges on a thorough understanding of its constituent elements.
- Standardization
- Data aggregation
- Accessibility
- Integration
- Collaboration
- Analysis
- Scalability
- Security
Standardization ensures consistent data formats, enabling integration across various systems. Data aggregation consolidates disparate sources, providing a comprehensive view. Accessibility allows authorized users to readily retrieve information. Integration connects diverse data streams for analysis. Collaboration fosters teamwork around data insights. Analysis extracts meaningful patterns and trends. Scalability accommodates future growth and data volume increases. Security protects sensitive information from unauthorized access, all crucial for a functioning SD Point Hub.
1. Standardization
Standardization of data points is fundamental to a functional SD Point Hub. Without consistent formats and definitions, data from diverse sources cannot be reliably combined, analyzed, or utilized effectively within the hub. This critical component directly impacts the hub's overall efficacy and the value it delivers.
- Data Format Consistency
Standardized data formats ensure compatibility across various data sources. For instance, if different departments use varying spreadsheet formats for recording production metrics, a unified CSV format enforced by the hub allows for easy import and aggregation. This avoids errors during data ingestion and analysis, improving the reliability of insights derived from the hub.
- Common Definitions and Units of Measurement
Standardizing definitions and units is equally critical. Different teams might use distinct terminology to describe similar processes or outputs. A standardized glossary and unit system ensure consistent interpretations throughout the hub, minimizing ambiguity and fostering accurate comparisons and analyses across departments or systems.
Read also:
- Augmented Reality Vs Justin Bieber Exploring The Intersection Of Technology And Pop Culture
- Data Validation Rules
Implementing data validation rules within the SD Point Hub ensures data accuracy and reliability. These rules, based on predefined criteria, automatically identify and flag data points that deviate from acceptable standards. This helps maintain data quality, leading to more trustworthy insights and decision-making processes.
- Impact on Data Integrity
Consistent data formats, definitions, and validation rules collectively enhance data integrity. The SD Point Hub, by enforcing standardization, minimizes errors, inconsistencies, and misinterpretations. This, in turn, promotes greater confidence in the information used for decision-making and process optimization.
In essence, standardization is the bedrock of a robust SD Point Hub. By establishing uniform data formats, definitions, and validation processes, the hub ensures data quality, facilitates seamless integration from diverse sources, and ultimately allows for more accurate and reliable insights. Without standardization, the SD Point Hub would become a repository of disparate and potentially unreliable data, significantly hindering its overall effectiveness.
2. Data Aggregation
Data aggregation is a crucial component of an effective SD Point Hub. It involves consolidating data points from various sources into a central repository, enabling comprehensive analysis and insights. The process is essential for drawing meaningful conclusions and making informed decisions.
- Centralized Data Repository
Data aggregation creates a centralized repository for diverse data points. This allows for a holistic view of information, transcending departmental or system boundaries. For instance, production data from multiple factories, sales figures from different regions, and customer feedback from various channels can all be brought together, enabling a comprehensive understanding of performance and trends.
- Standardized Data Formats
Data aggregation necessitates standardized formats for seamless integration. Different systems might use varied formats. By implementing standardized structures, the hub ensures compatibility among these data sources, avoiding inconsistencies and enabling efficient analysis.
- Improved Analysis and Insights
Aggregated data provides a broader context for analysis. Individual data points often lack significance in isolation. Aggregating them reveals patterns, trends, and correlations that would otherwise remain hidden. This enriched data set facilitates more robust and meaningful insights.
- Enhanced Decision-Making Capabilities
The holistic view offered by aggregated data empowers more informed decision-making. By combining data from various sources, stakeholders gain a clearer understanding of the overall performance and potential areas for improvement. This facilitates proactive strategies and more effective resource allocation.
In summary, data aggregation within an SD Point Hub is paramount. It provides a unified platform for consolidated data, fostering deeper analysis, more informed decisions, and ultimately improved performance. The comprehensive and standardized view offered through aggregation is critical for optimizing strategies and achieving desired outcomes.
3. Accessibility
Accessibility within an SD Point Hub is paramount. It dictates the ease with which authorized personnel can access, utilize, and manipulate the data held within the hub. Without appropriate access controls and user interfaces, the value of the centralized data repository diminishes significantly. A well-designed accessibility system ensures the hub serves its intended purpose efficiently and effectively.
- User Role-Based Access Control
Implementing user roles and associated permissions is essential. Different users (analysts, managers, executives) require varying levels of access. Restricting access to sensitive data based on roles prevents unauthorized modifications or viewing, upholding data integrity. For example, a production supervisor might need read-only access to quality control data, while a senior manager might require full access for strategic analysis. This granular control ensures data security and prevents breaches.
- Intuitive User Interface
An intuitive user interface is crucial for navigating and interacting with the hub's data. A user-friendly design, with clear visualizations and interactive tools, streamlines the data exploration process. This ensures authorized personnel can readily locate specific data points, generate reports, and carry out analyses. A poor interface can hinder productivity and negatively impact decision-making processes.
- Data Query and Retrieval Mechanisms
Efficient search and filtering capabilities empower users to quickly retrieve relevant data. The SD Point Hub should offer advanced search options, allowing users to apply complex criteria to isolate specific data sets. Robust query languages or intuitive filters enable users to drill down into granular details, facilitating insightful analysis. This direct access to needed information is vital for meeting deadlines and optimizing operational efficiency.
- Real-Time Data Updates and Dashboards
Providing real-time data updates and dynamic dashboards enhances responsiveness. This feature streamlines monitoring of key performance indicators and enables rapid identification of emerging trends. Updated dashboards offer a concise overview of current performance against goals, allowing for immediate adjustments and interventions where needed. The timeliness of data is crucial in dynamic environments.
In conclusion, the accessibility features of an SD Point Hub directly correlate with its overall value. By prioritizing user-friendly access controls, intuitive interfaces, and efficient data retrieval mechanisms, organizations can maximize the benefits of their centralized data repository. Effective accessibility ensures the hub serves its intended functionoptimizing decision-making and operational efficiencywhile minimizing administrative overhead.
4. Integration
Integration is a critical aspect of an effective SD Point Hub. The ability to seamlessly combine data from diverse sources is fundamental to the hub's functionality. Without robust integration mechanisms, the hub risks becoming a collection of isolated data points, hindering the analysis and insights it is designed to facilitate.
- Data Source Compatibility
Integration relies on the compatibility of various data sources. This includes ensuring that data formats, structures, and naming conventions are aligned. For instance, if manufacturing data is in a proprietary format and sales data in a standard CSV, the hub must translate and harmonize these different formats. Inconsistent or incompatible data structures lead to errors and hinder accurate analyses.
- Data Transformation and Mapping
Often, data from different sources requires transformation or mapping before integration. This can involve standardizing units of measurement, converting data types, or restructuring data fields. Consider aggregating production figures across different factory locations. The data may need standardization from different reporting systems, mapping them to a common format for the hub to aggregate and analyze effectively. Errors in transformation or mapping will introduce inaccuracies and lead to unreliable insights.
- API Integration and Data Exchange
Modern SD Point Hubs frequently utilize Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) for data exchange. This enables automated data transfer between systems and the hub. Efficient integration hinges on the use of well-defined APIs. Data exchange needs security protocols and data validation to ensure data integrity and prevent errors. Robust APIs facilitate the smooth and timely flow of data into and out of the hub, keeping it updated and accessible.
- System Orchestration and Automation
Integration extends beyond individual data points; it encompasses the orchestrated interaction between different systems. Automation plays a significant role in this process. Workflows are crucial to ensure timely data ingestion, transformation, validation, and updating of the hub. Automated processes minimize errors associated with manual data entry and enhance operational efficiency. This automated orchestration enables seamless data flow and efficient maintenance of the hub's integrity.
In conclusion, the integration capabilities of an SD Point Hub are fundamental to its success. Robust data source compatibility, efficient transformation and mapping, appropriate API integration, and streamlined system orchestration all contribute to a centralized, accurate, and dynamic data platform. This capability is not merely about combining data but also about facilitating the effective utilization of that combined data for insightful analysis, optimized processes, and informed decision-making.
5. Collaboration
A central data point hub fosters collaboration by providing a common platform for information sharing and analysis. The structured, accessible nature of the hub enables diverse teams to contribute, access, and interpret data in a coordinated manner. This shared understanding underpins collaborative problem-solving and decision-making.
Consider a manufacturing company with factories across multiple regions. An SD Point Hub, centralized and standardized, allows quality control data from each factory to be aggregated and analyzed collectively. This facilitates the identification of systemic issues and the implementation of cross-factory improvements. Sales teams can use the hub's data to understand regional performance trends and adjust strategies collaboratively. This shared data pool, managed by the hub, promotes coordinated efforts, maximizing overall efficiency and performance.
In essence, the effectiveness of an SD Point Hub directly correlates with the level of collaboration it facilitates. A well-designed hub with robust accessibility and integration features serves as a cornerstone for cross-functional teams to operate cohesively. The benefits extend beyond improved decision-making to include streamlined processes, reduced redundancies, and a shared understanding of key performance indicators. Addressing potential challenges, such as ensuring data security and maintaining user roles, is crucial for realizing the full collaborative potential of the hub and avoiding potential conflicts or data breaches. This illustrates how the hub facilitates collaboration, providing a shared landscape for all participants to thrive on. Successful implementations depend on acknowledging and addressing these considerations.
6. Analysis
The effectiveness of an SD Point Hub hinges significantly on the ability to conduct thorough and insightful analysis. A hub's value proposition lies in consolidating and standardizing data points, but true potential is unlocked through effective analysis. This analysis extracts meaningful patterns, identifies trends, and reveals actionable insights from the aggregated data. Without robust analytical capabilities, the hub remains a mere repository of data, failing to serve its primary purpose of optimizing decision-making and process improvement. The connection between analysis and the SD Point Hub is demonstrably strong and essential.
Real-world examples illustrate this link. A manufacturing company, utilizing an SD Point Hub to collect data on production output, quality control metrics, and equipment performance across various plants, can leverage analytical tools to identify correlations between equipment maintenance schedules and production yields. Identifying this correlation allows for proactive maintenance scheduling, minimizing downtime and maximizing output. Similarly, in a retail environment, analyzing sales data from different stores using a standardized SD Point Hub can reveal regional trends in consumer preferences. This information empowers targeted marketing campaigns, optimized inventory management, and ultimately, increased sales figures. In essence, the quality and depth of analysis directly dictate the practical value and utility derived from the SD Point Hub. Thorough analysis extracts actionable knowledge from aggregated data, leading to tangible benefits and improved decision-making.
In summary, analysis is not an add-on but a core function intrinsically linked to the SD Point Hub's purpose. Effective analysis extracts meaningful insights from the standardized data points, translating raw data into actionable knowledge. This knowledge directly impacts operational efficiency, strategic planning, and ultimately, the overall success of the organization. Failure to prioritize robust analytical tools and methods within the SD Point Hub framework will result in a less effective, less insightful, and ultimately, less valuable data repository. The connection between analysis and the SD Point Hub underscores the necessity for a comprehensive approach that prioritizes both data collection and analytical interpretation to maximize its impact and drive optimal business outcomes.
7. Scalability
Scalability is a critical component of an effective SD Point Hub. A hub's ability to accommodate increasing data volume, user base, and data complexity over time is paramount. A hub designed without scalability in mind will rapidly become a bottleneck, hindering operational efficiency and strategic decision-making as the organization grows and data sources proliferate. This inherent limitation severely restricts the long-term value of the investment.
Consider a manufacturing company expanding its global footprint. A scalable SD Point Hub can seamlessly integrate data from new factories, maintain data integrity, and continue to offer valuable insights even as production volumes increase. Without scalability, the hub would become a significant obstacle to managing operations and analyzing trends across the expanded network. Data integration would face increasing complexities, slowing responses to changing market demands. Similarly, a growing e-commerce company requires a scalable hub to handle the exponential increase in customer data, transaction records, and inventory levels. Without scalability, the system would struggle to maintain performance, ultimately compromising the ability to respond to market trends, optimize inventory, and deliver a positive customer experience.
In summary, scalability is an inherent requirement for a functional SD Point Hub. The ability to adapt to evolving data needs and organizational growth is essential. Understanding scalability's importance in the design and implementation of an SD Point Hub ensures long-term viability and ongoing value delivery. Organizations must anticipate future needs and incorporate scalable architecture into the design process to avoid unforeseen limitations and disruptions to operations as the volume and complexity of data increase. Robust scalability, therefore, ensures the SD Point Hub remains a dynamic asset throughout the organization's lifecycle.
8. Security
Data security is paramount for any system aggregating sensitive information, and a centralized data point hub (SD Point Hub) is no exception. Compromised data within such a hub can have severe consequences, potentially impacting operational efficiency, financial stability, and reputation. Implementing robust security measures is not an optional add-on but a fundamental requirement for a functioning and trustworthy SD Point Hub.
- Data Encryption and Access Control
Data encryption is crucial for protecting sensitive information held within the hub. Employing strong encryption algorithms ensures that even if unauthorized access is gained, the data remains unintelligible. Access control mechanisms, such as granular permissions based on user roles, are equally vital. Implementing strict protocols limits access to only authorized personnel, reducing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized modifications. For example, factory floor production data should have different access levels from executive-level financial data. Robust access control prevents accidental or malicious misuse of sensitive data points.
- Network Security and Infrastructure Protection
The network infrastructure supporting the SD Point Hub must be secured against external threats. Employing firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and secure network protocols is critical. Regular vulnerability assessments and penetration testing help identify and mitigate potential security gaps. The hub's physical location and physical security measures must also be considered. Protecting the hardware and preventing unauthorized access to the physical infrastructure is as crucial as securing the data itself. A secure network prevents outside attackers from reaching and compromising the hub.
- Data Integrity and Validation
Maintaining data integrity is essential to prevent manipulation or corruption. Employing data validation rules at the source and within the hub helps flag anomalies and inconsistencies. This proactive approach ensures that data ingested into the hub is accurate and reliable. This involves enforcing rules during data entry and aggregation to prevent errors or intentional manipulation. Consistent data validation safeguards against the introduction of incorrect or malicious data into the hub.
- Incident Response and Recovery Plan
A comprehensive incident response plan is crucial for handling security breaches. This plan outlines the steps to take in case of a security incident, including notification procedures, containment strategies, and recovery protocols. Regularly testing and updating this plan is vital to ensure preparedness and minimize the impact of any breach. A robust incident response plan prevents a localized issue from escalating into a major crisis. This plan provides a clear roadmap for handling security incidents, safeguarding the long-term operation of the SD Point Hub.
In conclusion, security is an integral part of a robust SD Point Hub. The interconnected nature of these security facetsencryption, network protection, data integrity, and incident responsecreates a layered defense. A strong security posture is not just a safeguard against external threats but a cornerstone of trust and reliability for the entire system. Prioritizing security ensures the ongoing functionality, reliability, and integrity of the SD Point Hub, enabling informed decision-making and optimal performance for the organization.
Frequently Asked Questions (SD Point Hub)
This section addresses common inquiries regarding SD Point Hubs. Clear and concise answers provide insight into the functionality, benefits, and implications of these systems.
Question 1: What is an SD Point Hub, and how does it differ from traditional data repositories?
An SD Point Hub is a centralized repository for standardized data points. It differs from traditional repositories by prioritizing standardized data formats, enabling seamless integration across various systems and departments. This standardization, combined with robust data aggregation capabilities, allows for more comprehensive analysis and insights compared to siloed data stores. Traditional repositories might contain data in various formats, hindering interoperability and potentially leading to inconsistencies in analysis. SD Point Hubs explicitly address this issue.
Question 2: What are the key benefits of using an SD Point Hub?
Key benefits encompass improved data consistency, enabling accurate and reliable analysis. Standardized data fosters collaboration among diverse teams. The centralized structure facilitates efficient data retrieval and enhanced reporting capabilities. Furthermore, a well-implemented SD Point Hub streamlines decision-making processes by providing a comprehensive, integrated view of organizational data. This, in turn, can lead to improved operational efficiency and reduced redundancies.
Question 3: How does an SD Point Hub ensure data security?
Data security is paramount. Robust security measures, including encryption, access controls, and regular audits, are implemented. User roles and permissions are carefully defined, limiting access to authorized personnel only. These security measures protect sensitive data from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure. This proactive approach to security mitigates risks and ensures the integrity of the data within the hub.
Question 4: What are the technical prerequisites for implementing an SD Point Hub?
Technical prerequisites involve selecting compatible data integration tools, ensuring data standardization across different systems, and designing a secure network infrastructure. Appropriate data transformation techniques and the ability to handle large volumes of data are critical for optimal functionality. A clear understanding of data governance and access control protocols is essential for effective implementation.
Question 5: How can an organization measure the ROI of an SD Point Hub implementation?
Measuring ROI involves evaluating improvements in operational efficiency, reduced redundancies in data management, improved accuracy of analysis, and enhanced decision-making capabilities. Quantifiable metrics, such as reduced errors, faster response times, and increased revenue attributed to data-driven insights, provide a concrete assessment of the hub's financial impact.
In conclusion, SD Point Hubs offer substantial advantages by centralizing and standardizing data. Careful consideration of technical requirements, security protocols, and data governance is crucial to maximizing return on investment. These factors contribute to a strong, reliable, and secure data infrastructure, fostering informed decision-making and organizational success.
This concludes the FAQ section. The next section explores specific implementation strategies for SD Point Hubs.
Conclusion
This exploration of SD Point Hubs has illuminated the critical role of centralized, standardized data repositories in contemporary organizations. Key aspects, including standardization, data aggregation, accessibility, integration, collaboration, analysis, scalability, and security, have been examined. The integration of diverse data sources into a single, unified platform has been shown to enhance data integrity, improve analytical capabilities, and foster inter-departmental collaboration. The ability of these hubs to adapt to growing data volumes and user bases is essential for their ongoing efficacy and value proposition. Robust security measures are not merely desirable but essential to safeguard sensitive information and maintain the integrity of the data within the hub. Standardization ensures consistent data formats, facilitating seamless integration, critical for accurate analysis and reliable insights. Addressing challenges in standardization and security ensures a secure and effective platform.
The implications for organizations are significant. Successfully implemented SD Point Hubs can dramatically improve operational efficiency, reduce redundancies, and promote strategic decision-making. By providing a holistic view of data, these centralized platforms allow organizations to make more informed and proactive decisions. The future success of organizations increasingly reliant on data-driven insights depends heavily on the effective implementation and utilization of SD Point Hub technology. Careful planning, thorough implementation, and ongoing maintenance are crucial for realizing the full potential of these systems. Further exploration of innovative analytical tools and integration techniques within these hubs will be key to advancing their potential in the coming years.