Accessing your Raspberry Pi remotely has become an essential skill for IoT enthusiasts and developers alike. Whether you're managing servers, automating home systems, or working on RemoteIoT projects, understanding how to remotely access Raspberry Pi is crucial. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know, from setting up your device to troubleshooting common issues.
As more people shift toward remote work and IoT development, the ability to remotely access Raspberry Pi has gained immense popularity. This capability allows users to control their devices from anywhere in the world, ensuring seamless management of IoT applications. From beginners to advanced users, this article provides detailed instructions and tips to make the process smooth and efficient.
This comprehensive guide not only explains the steps required to remotely access Raspberry Pi but also delves into the importance of secure connections and the tools available for downloading RemoteIoT software. By the end of this article, you'll be equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary to confidently manage your Raspberry Pi remotely.
Read also:Melissa Roxburgh Supernatural Unveiling The Stars Journey And Impact
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Remotely Accessing Raspberry Pi
- Setting Up Your Raspberry Pi for Remote Access
- Tools for Remote Access
- Ensuring Secure Connections
- Downloading RemoteIoT Software
- Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Advanced Techniques for Remote Access
- Best Practices for Remote Management
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
Introduction to Remotely Accessing Raspberry Pi
Why Remote Access Matters
Remote access to Raspberry Pi is vital for anyone working with IoT devices or managing servers. It allows users to control and monitor their devices without being physically present. This feature is particularly useful for developers and hobbyists who need to manage multiple devices simultaneously.
What You Need to Get Started
Before diving into the setup process, ensure you have the following:
- A Raspberry Pi device with Raspbian OS installed
- An active internet connection
- A static IP address or dynamic DNS service
- Basic knowledge of Linux commands
The Role of RemoteIoT Software
RemoteIoT software plays a critical role in enabling seamless remote access to Raspberry Pi. This software facilitates communication between devices and provides tools for monitoring and managing IoT applications.
Setting Up Your Raspberry Pi for Remote Access
Setting up your Raspberry Pi for remote access involves several key steps. Follow these instructions to ensure a smooth setup process:
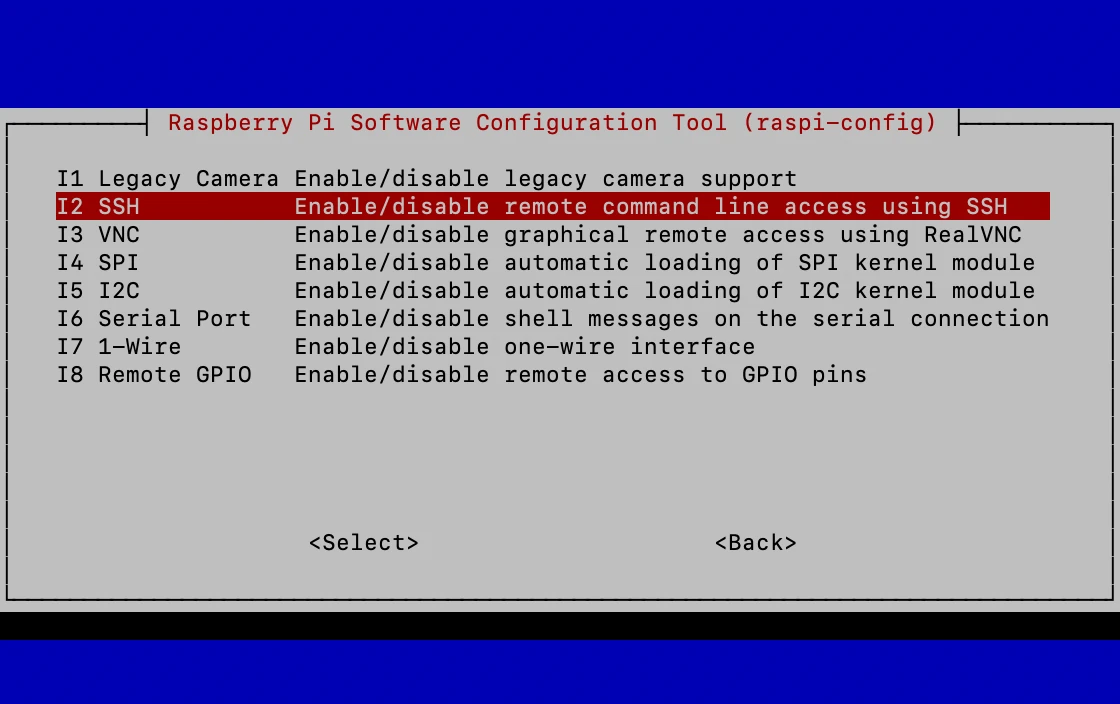
Step 1: Install SSH
SSH (Secure Shell) is a protocol that allows secure communication between devices. To enable SSH on your Raspberry Pi:
- Open the Raspberry Pi Configuration tool by typing
sudo raspi-configin the terminal. - Navigate to "Interfacing Options" and select "SSH".
- Choose "Yes" to enable SSH.
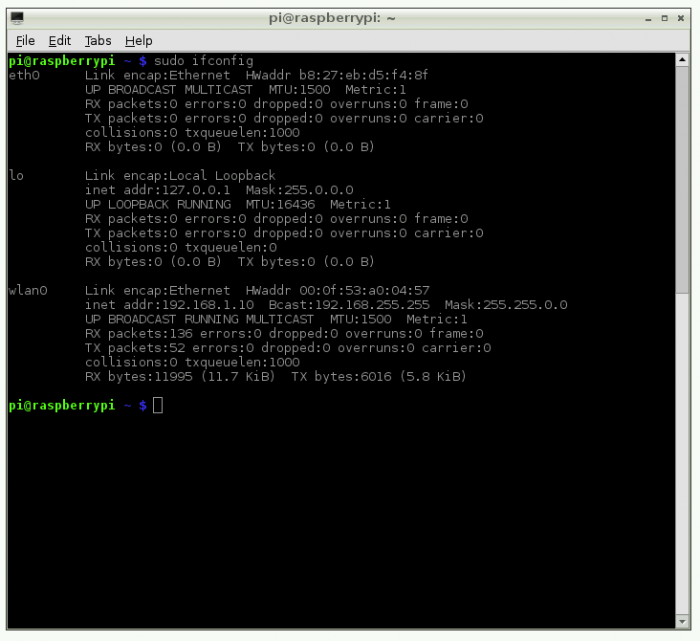
Step 2: Configure Your Network
Ensure your Raspberry Pi is connected to a stable network. You can either use a wired connection or configure Wi-Fi settings through the terminal.
Read also:Pink Hair The Ultimate Guide To Embracing Vibrant Beauty
Step 3: Assign a Static IP Address
A static IP address ensures that your Raspberry Pi remains accessible even if the network changes. Follow these steps to assign a static IP:
- Open the terminal and edit the
/etc/dhcpcd.conffile. - Add the following lines, replacing the placeholders with your network details:
interface eth0static ip_address=192.168.1.100/24static routers=192.168.1.1static domain_name_servers=192.168.1.1
Tools for Remote Access
Several tools are available for remotely accessing Raspberry Pi. Below are some of the most popular options:
1. PuTTY
PuTTY is a free and widely-used SSH client for Windows users. It allows you to connect to your Raspberry Pi from a remote computer.
2. VNC Viewer
VNC Viewer provides a graphical interface for remote access, making it ideal for users who prefer a GUI over the command line.
3. Web-Based Tools
Web-based tools like ngrok and localtunnel allow you to create secure tunnels for remote access without requiring complex configurations.
Ensuring Secure Connections
Security is paramount when remotely accessing Raspberry Pi. Follow these best practices to protect your device:
1. Use Strong Passwords
Create strong, unique passwords for your Raspberry Pi and avoid using default credentials.
2. Enable Two-Factor Authentication
Two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second form of verification.
3. Regularly Update Software
Keep your Raspberry Pi's operating system and installed software up to date to patch any security vulnerabilities.
Downloading RemoteIoT Software
RemoteIoT software is essential for managing IoT applications on Raspberry Pi. Here's how to download and install it:
Step 1: Access the Official Website
Visit the official RemoteIoT website and navigate to the download section.
Step 2: Choose the Correct Version
Select the version compatible with your Raspberry Pi's operating system.
Step 3: Install the Software
Follow the installation instructions provided on the website. Typically, this involves running a few commands in the terminal.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Encountering issues while setting up remote access is common. Below are solutions to some frequently encountered problems:
Issue 1: Unable to Connect via SSH
Ensure SSH is enabled on your Raspberry Pi and verify your IP address. If the problem persists, check your firewall settings.
Issue 2: Slow Connection Speeds
Optimize your network settings and consider using a wired connection for better performance.
Issue 3: Authentication Errors
Double-check your login credentials and ensure two-factor authentication is properly configured.
Advanced Techniques for Remote Access
For advanced users, there are several techniques to enhance remote access capabilities:
1. Port Forwarding
Configure your router to forward specific ports to your Raspberry Pi, allowing external access.
2. Use of SSH Tunnels
Create secure SSH tunnels to access services running on your Raspberry Pi from a remote location.
3. Automation Scripts
Develop automation scripts to streamline remote management tasks and reduce manual effort.
Best Practices for Remote Management
Adopting best practices ensures efficient and secure remote management of your Raspberry Pi:
1. Regular Backups
Perform regular backups of your Raspberry Pi's data to prevent loss in case of hardware failure.
2. Monitor System Performance
Use monitoring tools to track CPU usage, memory, and disk space to ensure optimal performance.
3. Document Configuration Details
Keep a record of all configuration settings and changes for future reference.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Can I access Raspberry Pi remotely without a static IP?
Yes, you can use dynamic DNS services to access Raspberry Pi remotely without a static IP.
Q2: Is VNC Viewer secure for remote access?
VNC Viewer is secure if configured correctly. Always use encryption and strong passwords to protect your connection.
Q3: How often should I update my Raspberry Pi's software?
It's recommended to update your Raspberry Pi's software at least once a month to ensure security and stability.
Conclusion
Remotely accessing Raspberry Pi for RemoteIoT download is a powerful tool for IoT enthusiasts and developers. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can set up secure and efficient remote access to your device. Remember to prioritize security and adopt best practices for seamless management.
We encourage you to share your experience or ask questions in the comments section below. Additionally, explore other articles on our site for more tips and tutorials on Raspberry Pi and IoT development. Together, let's build a smarter, more connected world!